REVIEW ARTICLE
The Diagnosis, Management and Complications Associated with Fractures of the Talus
Barnett J.R1, Ahmad MA1, Khan W2, *, O’ Gorman A.3
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2017Volume: 11
First Page: 460
Last Page: 466
Publisher ID: TOORTHJ-11-460
DOI: 10.2174/1874325001711010460
Article History:
Received Date: 06/02/2017Revision Received Date: 24/03/2017
Acceptance Date: 16/04/2017
Electronic publication date: 31/05/2017
Collection year: 2017

open-access license: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC-BY 4.0), a copy of which is available at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Fractures of the talus are uncommon injuries that can have devastating consequences. The blood supply to the talus is tenuous and injuries are associated with a higher incidence of avascular necrosis and malunion. Talar neck fractures are the most common fractures. This review looks at the different types of fractures of the talus, particularly focusing on talar neck fractures. The diagnosis and management are discussed as well as the complications.
1. INTRODUCTION
Fractures of the talus are uncommon, accounting for approximately 0.1% of all fractures. The talus is the second most common tarsal bone to be injured after the calcaneus [1]. Fractures of the talus are associated with significant morbidity in view of the blood supply, and these can be challenging for surgeons to manage [2]. The talus is a dense bone and fractures in non-pathological bone usually result from high energy impacts e.g. motor vehicle collisions or a fall from a significant height [3]. Fractures of the talus were first described in parachutists and pilots of the Royal Air Force who sustained these injuries upon impact with the ground, hence termed aviator’s astragalus [4, 5].
Fractures of the talus can be classified by their anatomical locations, and include talar neck, head, body, lateral process and posterior process fractures. Of these fractures, talar neck fractures are the most common. Elgafy et al (2000) found that talar neck fractures constituted 45% of talar fractures in their study of 60 patients [6]. Snowboarders are at increased risk of lateral process fractures due to the forces involved in landing a jump and the position of the feet when hitting the ground [7].
The results with surgical management of these fractures have improved over the last few years, largely due to a greater understanding of the anatomy of the region [8]. Optimal reduction often necessitates both anteromedial and anterolateral exposures during reduction and fixation [8]. This method of reduction and fixation is a possible explanation for reduced morbidity and better results. In this review paper, we describe the anatomy and clinical presentation of these injuries.
2. ANATOMY
The talus is the tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint. Its biomechanical role includes the transmission of forces between the lower leg and the foot. It does not have any musculotendinous attachments [2].
The talus is anatomically composed of three parts, the body, neck and head. Fig. (1a) shows the superior view of the talus and Fig. (1b) shows the inferior view. The talar body articulates with the tibia superiorly at the ankle joint, and with the calcaneus inferiorly at the subtalar joint. The talar head articulates with the navicular anteriorly. The talar neck, between the head and the body, faces anteromedially [2] and forms the weakest part of the bone [3]. Fig. (1) shows that the talus is widest at the anterior aspect, limiting rotational movements when the foot is dorsiflexed and conferring greater stability. In dorsiflexion, the talar dome forces the fibula laterally into external rotation. In plantar flexion the ankle’s ligamentous attachments provide joint stability. These include the deltoid ligament medially and the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle laterally [2].
The blood supply to the talus was described by Wildenauer and then by Haliburton in the 1950s [9]. The arteries that supply the talus are the posterior tibial, the anterior tibial and the perforating peroneal arteries [1]. There is an anastomotic ring that surrounds the talar head and neck and supplies the talar body. Almost 60% of the talus is covered with articular cartilage, and only a small portion of the talus may be perforated by blood vessels. This makes it more prone to avascular necrosis [3]. Additionally where there is a talar neck fracture, the intraosseus branches and artery to the tarsal canal (a branch of the posterior tibial artery) are disrupted. The talar body then only receives blood from the deltoid branch of the posterior tibial artery. This usually supplies the talar body posteromedially and therefore the risk of avascular necrosis is increased [10].
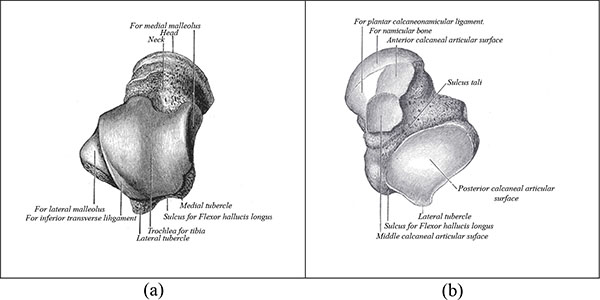 |
Fig. (1). Anatomy of the talus with (a) a superior view, and (b) an inferior view. |
3. TALAR NECK FRACTURES
These are the most common fracture of the talus, accounting for approximately half of all talar fractures [11]. The consequences of a talar neck fracture may be devastating due to the significant complications that can arise following this injury. These include avascular necrosis, mal-union and arthritis [12]. Halvorsen et al in a systemic review of 848 patients with talar neck fractures reported a 33% incidence of avascular necrosis, 17% incidence of mal-union and 70% cases resulted in a post-traumatic arthrosis [12].
3.1. Mechanism of Injury
Talar neck fractures typically result from high energy trauma such as motor vehicle collisions. The mechanism is usually forced dorsiflexion of the foot as the talar neck is forced against the tibial crest [5]. This may occur when the driver exerts pressure on the brake pedal during a collision [5]. This was the mechanism described by Anderson where pilots exerted pressure on the rudder pedal as they crashed to the ground [5, 11]. A caderveric study by Funk et al simulated this mechanism of injury. A pedal was driven towards the knee causing dorsiflexion and axial loading. They reported both talar neck fractures and medial malleolar fractures occurring [13].
3.2. Classification
Hawkins described a classification for these factures in 1970 which remains in use today [14, 15]. The classification uses plain radiography to assess the severity of the fracture to the talar neck. Fig. (2). Type 1 fracture is non-displaced. Type 2 has displacement of the fracture with subluxation/dislocation of the subtalar joint. Type 3 is similar to type 2, with additional subluxation/dislocation of the ankle joint [15]. Type 4 is a modification later added to the Hawkins classification and includes type 3 with talonavicular dislocation [16]. Type II fractures have been further divided by Vallier et al into IIa and IIb. The IIa fracture does not include subtalar dislocation whereas IIb does. They observed an increased rate of avascular necrosis where the subtalar joint was dislocated [17].
Halvorsen et al in their systematic review showed an increasing trend of avascular necrosis with each Hawkins type. This was 5.7% for Hawkins type 1, 18.4% for Hawkins type 2 and 44.7% for Hawkins type 3. This percentage drops to 12% for type 4 fractures which the authors felt may have been influenced by the rarity of the injury, there were only 33 cases in 848 patients [12].
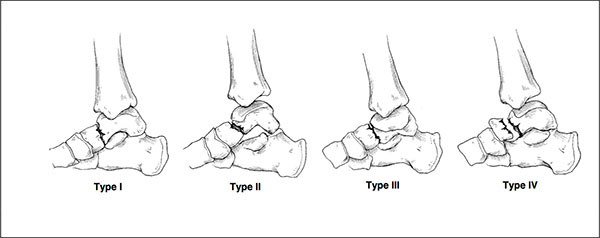 |
Fig. (2). Diagrammatic representation of talar neck fractures by Fortin et al (1). |
3.3. Clinical Presentation
Due to the high energy required to fracture the talus, these fractures may be part of a multi-trauma presentation. There may be significant deformity necessitating immediate reduction to prevent skin necrosis [1].
The injury tends to cause pain and swelling to the ankle with the inability to bear weight. Examination will usually reveal tenderness in the ankle region with a reduced range of movement. The talar head and neck may be palpated anterior and inferior to the ankle joint. The body may be palpated distal to the malleoli and anterior to the Achilles tendon [18]. As with all orthopaedic examinations assessing the neurovascular status is essential and any deficit will require urgent intervention.
3.4. Imaging
Imaging is initially undertaken with plain radiography. The views required are anterior-posterior, lateral and mortise. Plain radiographs may detect talar neck fractures but there is a high false negative rate. A study of 132 talar fractures found that 93% had additional fracture information on Computerised Tomography (CT) scanning that was not found on initial plain radiography [19]. Canale et al. advise special talar views that involve taking oblique x-rays of the foot to further evaluate the talar neck. This shows the calcaneus below the talar head and neck. The ankle is fully plantar flexed with pronation of the foot at 15 degrees. The inferior aspect of the foot is placed on the x-ray table. X-rays are then projected at a 75 degree angle to the table [16].
Further characterisation of the fracture may be carried out with CT scanning. Where a fracture is suspected or confirmed on X-ray, Fig. (3), a CT scan should be obtained. A missed talar fracture, even with minimal displacement may have severe long term consequences [1]. A study by Rodop et al found that 39% of ankle and midfoot fractures may be missed at this initial stage. In their small study, they found eight cases that were missed initially on plain radiography. These patients were at first treated conservatively. They were eventually diagnosed through Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and CT scanning [21]. They concluded that if there remains suspicion about a talar fracture then further imaging is recommended to reduce the risk of complications. These imaging modalities may also be beneficial for operative planning [22].
MRI scanning is not usually used in the early stage. It tends to be used where patients continue to complain of symptoms 4-6 weeks following injury in the presence of normal radiographs. It may then be useful to evaluate soft tissues, articular surfaces and possible bony injury [23].
 |
Fig. (3). Fracture to the talar neck [20]. |
3.5. Management
Fractures of the talus are high energy injuries and the patient may often present as a polytrauma with life or limb threatening injuries. In some situations, life and limb saving treatments take priority, but as soon as is safe to do so, this injury should be assessed and managed. Treatment of fractures of the talus depends on the location of the fracture [1]. Where there is an open fracture, neurovascular deficit or dislocation, immediate treatment is required. An undisplaced talar neck fracture where there is adequate alignment of articular surfaces may be treated non-operatively. A cautious approach is required as even minimal displacement may require surgical fixation to avoid complications [1]. Type II-IV fractures require immediate fixation in order to reduce the incidence of complications. This is by open reduction and internal fixation [16]. A French multicentre study of 114 patients looked at internal fixation of both talar neck and body fractures with a five-year follow-up. They found that reduction quality was better with K-wire fixation than screws using the Kitaoka score. Screws could cause excessive compression, especially where comminution was present [22]. They recommended using screws for simple fractures and plates where there is comminution.
Dealing with the complications after a fracture of the talus may necessitate further procedures. In the study by Canale, 25% of patients who had avascular necrosis, malunion, arthritis and infection required a further procedure [16].
In order to identify avascular necrosis of the talus, Hawkins sign may be used. This is seen as a radiolucent band on a radiograph 6-8 weeks following a fracture. Its presence indicates subchondral atrophy and that the talus is unlikely to develop avascular necrosis as there is sufficient vascularity. It has been shown by Tezvel et al in a study of 26 patients to have a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 57.7% [24]. In those who have undergone avascular necrosis of the talus a number of options are available. These include talectomy, pantalar arthrodesis, tibiotalar arthrodesis and tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis. Dennison et al report good functional outcome following excision of the necrotic body of the talus with tibiocalcaneal fusion using an Ilizarov frame [25].
4. TALAR BODY FRACTURES
These fractures account for approximately 20% of all fractures of the talus [6]. Fracture of the talar body is not an isolated phenomenon; Sneppen & Buhl [26] found that forces that act upon the talus and result in fractures also affect, and sometimes fracture, the ankle joint. Fractures of the talar body can be classified as compression injuries, shear fractures, fracture of the posterior process, fracture of the lateral process and crush fractures. Talar body fractures have a similar mechanism of injury as talar neck fractures. They tend to occur following axial loading on the ankle through the leg although the foot is not dorsiflexed. They usually involve the articular surfaces, primarily the ankle joint and occasionally the subtalar joint. This increases the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis [27].
These fractures are nearly always managed operatively. Despite this, there is a high rate of complications [8]. These patients may develop osteoarthritis. Vallier et al found that 17 of 26 patients developed osteoarthritis of the tibiotalar joint, and nine of 26 patients developed osteoarthritis of the subtalar joint (8). There is a high incidence of disruption to the blood supply and the rate of avascular necrosis has been reported at 25% [27].
5. TALAR HEAD FRACTURES
The talar head is the least common part of the talus to fracture. In 228 patients with talar fractures, only 2.6% had a fracture of the talar head [4]. They are usually sustained when the foot is plantar flexed and there is a forced axial load. They tend to be intra-articular injuries and may extend to the neck and body. They are associated with dislocation or subluxation of the talus [1]. Long et al describe two patient groups. Older osteoporotic patients who undergo an insufficiency fracture with minimal activity and younger patients sustaining high-energy injuries [28]. The talar head receives a good blood supply that makes it less likely to undergo avascular necrosis than talar neck or body fractures [27].
Talar head fractures may be managed non-operatively or operatively. The aim of treatment is to preserve the articular surfaces and ensure stability of the talonavicular joint. A non-displaced and isolated impaction fracture or an avulsion fracture with no extension into the subtalar joint with minimal disruption of the talonavicular surface can be managed conservatively. For all other talar head fractures, operative fixation is advised [18].
6. LATERAL PROCESS FRACTURES
The lateral process of the talus is a wedge shaped prominence that protrudes from the body of the talus. It forms part of the subtalar joint as it articulates with the fibula laterally and the os calcis inferiorly [29]. Fractures of the lateral process are common in snowboarders. They have been shown to account for 15% of ankle injuries in snowboarders due to the impact of landing from jumps [30]. The mechanism of injury involves inversion and dorsiflexion of the ankle whilst applying an axial load [7, 31]. They may be difficult to diagnose on plane x-ray and clinically can appear similar to an ankle sprain. CT scanning is advised where there is concern [32].
The McRory-Bladin classification describes three types of fracture [31]. Type I fractures do not involve articular surfaces. Type 2 fractures involve the joint surface of the ankle and the subtalar joint. Type 3 fractures involve comminution.
Management may be non-operative or operative. Where a fracture is non-displaced and small, it may be managed with cast immobilisation. Larger fractures and displaced fractures are treated with open reduction and internal fixation [33, 34]. Lateral process fractures may be complicated by osteoarthritis and malunion. Koch et al found that 45% of patients with this injury were associated with subtalar osteoarthritis [34].
CONCLUSION
Talar fractures are infrequent but potentially devastating injuries. Talar neck fractures are by far the most common, accounting for 50% of these injuries, and are classified using Hawkins classification. The vascular supply of the talus is such that fractures to the neck and body have a high likelihood of developing avascular necrosis. Other complications of talar fractures include non-union, malunion and osteoarthritis. Operative fixation is used in most cases of talar fractures. Treatment should be expedited where there is evidence of neurovascular deficit or open injury.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author confirms that this article content has no conflict of interest
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.
REFERENCES
| [1] | Fortin PT, Balazsy JE. Talus fractures: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2001; 9(2): 114-27. |
| [2] | RW B. Rockwood and Green’s fractures in adults. 7th Edition ed. Philadelphia:: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2001. July 2002 |
| [3] | Adelaar RS, Madrian JR. Avascular necrosis of the talus. Orthop Clin North Am 2004; 35(3): 383-95. [xi.]. |
| [4] | Coltart WD. Aviator's astragalus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1952; 34-B(4): 545-66. |
| [5] | Anderson HG. The Medical and Surgical Aspects of Aviation. London: Henry Frowde, Oxford University Press 1919. |
| [6] | Elgafy H, Ebraheim NA, Tile M, Stephen D, Kase J. Fractures of the talus: experience of two level 1 trauma centers. Foot Ankle Int 2000; 21(12): 1023-9. |
| [7] | Chan GM, Yoshida D. Fracture of the lateral process of the talus associated with snowboarding. Ann Emerg Med 2003; 41(6): 854-8. |
| [8] | Vallier HA, Nork SE, Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Surgical treatment of talar body fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004; 86-A(Suppl. 1(Pt 2)): 180-92. |
| [9] | Haliburton R, Sullivan R. The Extra-osseous and Intra-osseous Blood Supply of the Talus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1958; 40A(5): 1115-20. |
| [10] | Lin SS, Montemurro NJ. New modification to the Hawkins classification scheme is more predictive of osteonecrosis: commentary on an article by Heather A. Vallier, MD, et al.: “A new look at the Hawkins classification for talar neck fractures: which features of injury and treatment are predictive of osteonecrosis? J Bone Joint Surg Am 2014; 96(3): e25. |
| [11] | Archdeacon M, Wilber R. Fractures of the talar neck. Orthop Clin North Am 2002; 33(1): 247-62. [x.]. |
| [12] | Halvorson JJ, Winter SB, Teasdall RD, Scott AT. Talar neck fractures: a systematic review of the literature. J Foot Ankle Surg 2013; 52(1): 56-61. |
| [13] | Funk JR, Rudd RW, King RJ, Srinivasan SC, Bailey AM, Crandall JR. Injuries caused by brake pedal loading of the midfoot. Biomed Sci Instrum 2012; 48: 134-40. |
| [14] | Canale ST. Fractures of the neck of the talus. Orthopedics 1990; 13(10): 1105-15. |
| [15] | Hawkins LG. Fractures of the neck of the talus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970; 52(5): 991-1002. |
| [16] | Canale ST, Kelly FB Jr. Fractures of the neck of the talus. Long-term evaluation of seventy-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1978; 60(2): 143-56. |
| [17] | Vallier HA, Reichard SG, Boyd AJ, Moore TA. A new look at the Hawkins classification for talar neck fractures: which features of injury and treatment are predictive of osteonecrosis? J Bone Joint Surg Am 2014; 96(3): 192-7. |
| [18] | Koehler S. Talus fractures: Wolters Kluwer; 2013 [cited 2015] Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/talus-fractures 2013. |
| [19] | Dale JD, Ha AS, Chew FS. Update on talar fracture patterns: a large level I trauma center study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013; 201(5): 1087-92. |
| [20] | Buckley R, Strands A. Talus-Displaced neck fracture [cited 2015] Available from: https://www2.aofoundation.org/ wps/portal/surgery/?showPage= redfix&bone= Foot&segment= Talus&classification= 81-Neck+fractures&treatment=&method= Displaced+ fractures&implantstype=ORIF+-+screw+fixation&redfix_url=1283868262857 2015. |
| [21] | Rodop O, Mahiroğulları M, Akyüz M, Sönmez G, Turgut H, Kuşkucu M. Missed talar neck fractures in ankle distortions. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2010; 44(5): 392-6. |
| [22] | Fournier A, Barba N, Steiger V, Lourdais A, Frin JM, Williams T, et al. Total talar fracture - long-term results of internal fixation of talar fractures. A multicentric study of 114 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2012; 98(4)(Suppl.): S48-55. |
| [23] | Beltran J, Shankman S. MR imaging of bone lesions of the ankle and foot. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2001; 9(3): 553-66. |
| [24] | Tezval M, Dumont C, Stürmer KM. Prognostic reliability of the Hawkins sign in fractures of the talus. J Orthop Trauma 2007; 21(8): 538-43. |
| [25] | Dennison MG, Pool RD, Simonis RB, Singh BS. Tibiocalcaneal fusion for avascular necrosis of the talus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2001; 83(2): 199-203. |
| [26] | Sneppen O, Buhl O. Fracture of the Talus-A study of its genesis and morphology based upon cases with associated ankle fracture. Acta Orthop Scand 1974; 45: 307-20. |
| [27] | Higgins TF, Baumgaertner MR. Diagnosis and treatment of fractures of the talus: a comprehensive review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int 1999; 20(9): 595-605. |
| [28] | Long NM, Zoga AC, Kier R, Kavanagh EC. Insufficiency and nondisplaced fractures of the talar head: MRI appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012; 199(5): W613-7. |
| [29] | LG. Fracture of the lateral process of the talus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1965; 47: 1170-5. |
| [30] | Kirkpatrick DP, Hunter RE, Janes PC, Mastrangelo J, Nicholas RA. The Snowboarder’s Foot and Ankle. Am J Sports Med 1998; 26(2): 271-7. |
| [31] | Perera A, Baker JF, Lui DF, Stephens MM. The management and outcome of lateral process fracture of the talus. Foot Ankle Surg 2010; 16(1): 15-20. |
| [32] | Noble J, Royle SG. Fracture of the lateral process of the talus: computed tomographic scan diagnosis. Br J Sports Med 1992; 26(4): 245-6. |
| [33] | Tucker DJ, Feder JM, Boylan JP. Fractures of the lateral process of the talus: two case reports and a comprehensive literature review. Foot Ankle Int 1998; 19(9): 641-6. |
| [34] | Knoch Fv, Reckord U, Knoch Mv, Sommer C. Fracture of the lateral process of the talus in snowboarders. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007; 89(6): 772-7. |








